Gabapentin 100mg for Spinal arthritis, also known as osteoarthritis of the spine, can cause debilitating pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. For those struggling with chronic discomfort, finding an effective treatment is crucial. One medication often prescribed for nerve-related pain is Gabapentin (brand name Neurontin). But can Gabapentin 100mg truly help manage spinal arthritis pain?
In this detailed guide, we’ll explore:
- How Gabapentin works for spinal arthritis
- The effectiveness of Gabapentin 100mg for pain relief
- Dosage recommendations and safety considerations
- Potential side effects and precautions
- Lifestyle tips to enhance Gabapentin’s benefits
Let’s dive in.
How Gabapentin Works for Spinal Arthritis Pain
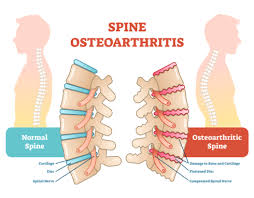
Gabapentin (Neurontin) is primarily an anticonvulsant drug, but it’s also widely used for neuropathic pain—pain caused by nerve damage or irritation. Spinal arthritis often leads to nerve compression (such as in spinal stenosis or herniated discs), resulting in shooting pain, tingling, or burning sensations.
Gabapentin works by:
- Calming overactive nerves – It binds to calcium channels in the brain and spinal cord, reducing abnormal electrical activity that contributes to pain signals.
- Decreasing central sensitization – Chronic pain can make the nervous system hypersensitive; Gabapentin helps normalize this response.
While it doesn’t directly treat joint inflammation like NSAIDs or steroids, it can significantly reduce nerve-related pain associated with spinal arthritis.
Is Gabapentin 100mg Effective for Spinal Arthritis Pain?
The dosage of Gabapentin varies depending on pain severity and individual response. Gabapentin 100mg is a starting dose, often gradually increased under medical supervision.
What Research Says:
- Studies show Gabapentin can help with chronic neuropathic pain, including pain from spinal conditions.
- Some patients report reduced radiating pain, numbness, and tingling at lower doses (100 mg- 300 mg).
- Higher doses (up to 3600mg/day in divided doses) may be needed for severe pain, but starting low minimizes side effects.
Patient Experiences:
- Many find Gabapentin 100mg helpful for mild to moderate nerve pain.
- Some require dose adjustments for optimal relief.
- Effects may take a few weeks to fully manifest.
Key Takeaway: While Gabapentin 100mg may not be strong enough for severe spinal arthritis pain, it can be a good starting point, especially for those with nerve-related symptoms.
Recommended Dosage & How to Take Gabapentin Safely
Starting Dose for Spinal Arthritis Pain:
- 100mg to 300mg per day, taken at bedtime (to minimize drowsiness).
- Gradually increased by 100mg every 3-7 days based on tolerance.
- Maintenance dose typically ranges from 300mg to 1800mg daily (divided into 3 doses).
Important Guidelines:
Take with food to improve absorption.
Avoid sudden stops—taper off slowly to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Monitor for side effects (dizziness, fatigue, swelling).
Potential Side Effects of Gabapentin 100mg
While generally well-tolerated, Gabapentin may cause:
- Common: Drowsiness, dizziness, mild fatigue.
- Less Common: Swelling in extremities, blurred vision, weight gain.
- Rare but Serious: Mood changes (anxiety, depression), allergic reactions.
Precautions:
- Avoid alcohol (increases drowsiness).
- Inform your doctor if you have kidney issues (dose adjustments may be needed).
Enhancing Gabapentin’s Effects: Lifestyle Tips for Spinal Arthritis
To maximize pain relief, combine Gabapentin with:
1. Physical Therapy & Gentle Exercise
- Stretching, yoga, and low-impact activities (swimming, walking) can reduce stiffness.
2. Heat & Cold Therapy
- Heat relaxes muscles; ice reduces inflammation.
3. Posture Correction & Ergonomics
- Use lumbar support, and avoid prolonged sitting.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Omega-3s, turmeric, and leafy greens may help reduce joint stress.
Final Verdict: Should You Try Gabapentin 100mg for Spinal Arthritis?
Gabapentin (Neurontin) 100mg can be a useful option for nerve-related spinal arthritis pain, especially if you experience:
Shooting or burning pain
Tingling/numbness in limbs
Pain that worsens at night
However, it may not be sufficient alone for severe cases. Always consult your doctor before starting or adjusting your dose.