Thermoplastic polyester elastomer (TPEE) is an advanced polymer material characterized by its flexible yet strong nature, combining hard crystalline segments and soft amorphous segments. It is increasingly favored for its high mechanical performance, chemical resistance, and ease of processing through conventional thermoplastic techniques such as injection molding, extrusion, and rotational molding. The global market for TPEE has been growing steadily, driven primarily by expanding applications in the automotive, electrical and electronics, industrial, and medical sectors, and it is projected to continue this growth trajectory through 2033 at a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 6.9%.
Market Size and Forecasts
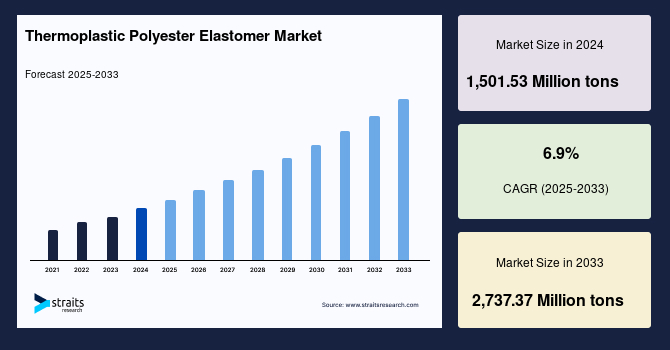
The Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomer Market size was valued at 1404.61 Million tons in 2024 and is predicted to reach from 1501.53 Million tons by 2025 to 2560.68 Million tons by 2033, increasing at a CAGR of 6.9% from 2025 to 2033.
Material Characteristics and Processing Advantages
TPEE is composed of crystalline polybutylene terephthalate (hard segment) and polyether (soft segment), making it both tough and flexible. It can endure high temperatures and resist tearing, flex cut growth, creep, and abrasion, while also exhibiting strong resistance to hydrocarbons and lubricants. These properties make TPEE particularly suited for manufacturing automotive components, electrical equipment housings, and high-performance consumer products. The polymer can be processed by standard thermoplastic methods including injection molding and extrusion, which facilitate efficient production and design flexibility.
Key Applications Driving Market Growth
Automotive Industry: The automotive sector remains the dominant end-user of TPEE globally. Increasing production of passenger and commercial vehicles fueled by the demand for lightweight, durable materials has significantly contributed to TPEE consumption. Automakers prefer thermoplastic parts for their ability to lower production costs and enhance fuel efficiency through weight reduction. Applications include connectors, plugs, housing components, safety belt tensioners, airbags, and window motor housings.
Electrical & Electronics: Usage of TPEE in consumer electronics, home appliances, and electrical components has risen, attributed to its excellent electrical insulation, dimensional stability, and high thermal distortion temperature. Circuit breakers, switches, and various connectors are increasingly made from TPEE compounds.
Medical Sector: Rising healthcare expenditure and the need for lightweight, sterile medical devices have prompted growth in TPEE use in manufacturing surgical gloves, plastic syringes, instruments, and pharmaceutical packaging. Its chemical stability and lightweight properties enhance usability and transportation efficiency.
Consumer Goods and Industrial Applications: TPEE is also gaining traction in industrial machinery, footwear, sporting goods, and packaging sectors due to its flexibility, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. Novel applications involving biodegradable and biobased TPEE variants are also emerging, catering to sustainability trends.
Regional Market Insights
North America stands as the largest regional market for thermoplastic polyester elastomers, driven by strong automotive, construction, electrical, and packaging industries. The preference for plastic automotive parts that reduce cost and increase profitability supports this leadership. Canada’s crude oil production facilitates raw material availability, further supporting market growth.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing market region, led by China, India, and Southeast Asia. Expansion in automotive manufacturing, electrical and electronics production, and industrial machinery sectors underpins growth. The region benefits from lower labor and raw material costs, accelerating TPEE adoption.
Europe holds a significant share with steady growth led by manufacturing in Eastern Europe despite economic challenges. This region faces strict environmental regulations that influence market dynamics and encourage innovation in sustainable TPEE products.
Emerging regions, including Latin America and the Middle East & Africa, are showing rapid growth prospects, bolstered by increasing industrial activities and lower market penetration, representing substantial potential for expansion.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
While TPEE offers numerous advantages, its production remains more costly and complex than conventional plastics due to high-tech manufacturing requiring elevated temperatures. This has limited broader adoption to relatively high-end applications so far. Additionally, competition from substitute elastomers and restructuring activities among suppliers create market pressures.
On the opportunity side, the ongoing development of biobased TPEE and TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) products responsive to environmental sustainability goals is a crucial growth avenue. These bio-sourced materials promise enhanced biodegradability and reduced dependence on fossil resources, appealing to environmentally conscious sectors like electronics, automotive, and footwear.
Leading manufacturers are investing in new formulations and technologies to improve performance characteristics and cost-efficiency. The substitution of traditional heavy materials such as metals and wood with TPEE in diverse applications is expected to further propel market expansion.
Conclusion
The thermoplastic polyester elastomer market is poised for significant growth across multiple industries with a forecast CAGR of approximately 6.9% through 2033. Its unique combination of flexibility, strength, and thermal and chemical resistance is driving adoption in automotive, electrical, healthcare, and consumer goods sectors. While production costs and competitive substitutes remain challenges, innovation in biobased materials and expanding end-use applications offer promising opportunities for market players worldwide. Regional dynamics with North America leading in market size and Asia Pacific driving rapid growth highlight diverse opportunities tailored to specific industrial and economic conditions globally. This outlook positions TPEE as a key material in the future of lightweight, sustainable manufacturing technologies.